What is WebRTC
WebRTC (Web Real-Time Communications) is an open source project that enables real-time voice, text and video communications capabilities between web browsers and devices. WebRTC provides software developers with application programming interfaces (APIs) written in JavaScript.
Developers use these APIs to create peer-to-peer (P2P) communication between internet web browsers and mobile applications without worrying about compatibility and support for audio, video or text based content.
With WebRTC, data transfer occurs in real time without the need for a custom interface, extra plugins or special software for browser integration. WebRTC enables real-time audio and video communication simply by opening a webpage.
How does WebRTC work
WebRTC uses JavaScript, APIs and Hypertext Markup Language to embed communications technologies within web browsers. It is designed to make audio, video and data communication between browsers user-friendly and easy to implement. WebRTC works with most major web browsers.
WebRTC APIs perform several key functions, including accessing and recording video, audio, and text based data from device to initiating, monitoring and ending P2P connection between devices via browser and facilitating bidirectional data transfer over multiple data channels.
In most cases, WebRTC connects users by transferring real-time audio, video and data from device to device using P2P communications. In situations where users are on different Internet Protocol (IP) networks that have Network Address Translation (NAT) firewalls that prevent RTC, WebRTC can be used in conjunction with Session Traversal Utilities for NAT (STUN) servers. This enables a given IP address to be translated into a public internet address so peer connections can be established.

The Interactive Connectivity Establishment protocol is used to find the best connection.
WebRTC Protocols
ICE (Interactive Connectivity Establishment)
Interactive Connectivity Establishment (ICE) is a framework to allow your web browser to connect with peers. There are many reasons why a straight up connection from Peer A to Peer B won’t work. It needs to bypass firewalls that would prevent opening connections, give you a unique address if like most situations your device doesn’t have a public IP address, and relay data through a server if your router doesn’t allow you to directly connect with peers. ICE uses STUN and TURN server to accomplish this.
STUN (Session Traversal Utilities for NAT)
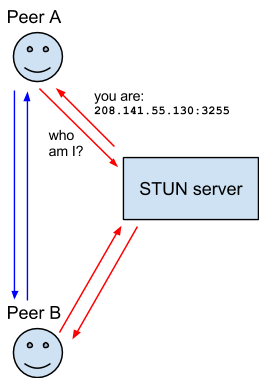
Session Traversal Utilities for NAT (STUN) is a protocol to discover your public address and determine any restrictions in your router that would prevent a direct connection with a peer.
The client will send a request to a STUN server on the internet who will reply with the client’s public address and whether or not the client is accessible behind the router’s NAT.
NAT (Network Address Translation )
Network Address Translation (NAT) is used to give your device a public IP address. A router will have a public IP address and every device connected to the router will have a private IP address. Requests will be translated from the device’s private IP to the router’s public IP with a unique port. That way you don’t need a unique public IP for each device but can still be discovered on the internet.
Some routers will have restrictions on who can connect to devices on the network. This can mean that even though we have the public IP address found by the STUN server, not anyone can create a connection. In this situation we need to use TURN.
TURN (Traversal Using Relays around NAT)
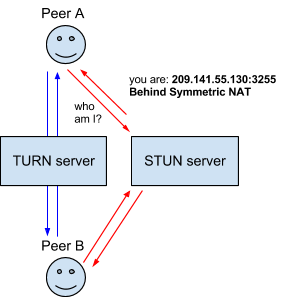
Some routers using NAT employ a restriction called ‘Symmetric NAT’. This means the router will only accept connections from peers you’ve previously Connected to.
Traversal Using Relays around NAT (TURN) is meant to bypass the Symmetric NAT restriction by opening a connection with a TURN server and relaying all information through that server. You would create a connection with a TURN server and tell all peers to send packets to the server which will then be forwarded to you. This obviously comes with some overhead so it is only if there are no other alternatives.
SDP (Session Description Protocol)
Session Description Protocols (SDP) is a standard for describing the multimedia content of the connection such as resolutions, formats, codecs, encryption etc. so that both peers can understand each other once the data is transferred. This is, in essence, the metadata describing the content and not the media content itself.
What is WebRTC used for
The goal of WebRTC is to facilitate real-time P2P communication over the internet. There are several use cases for WebRTC, including the following:
• WebRTC is used for video chats and meetings on video calling platforms, such as Zoom, Microsoft Teams, Slack or Google Meet.
• Industries, including healthcare, surveillance and monitoring, and internet of things, use WebRTC.
• In the field of home and business security and surveillance, WebRTC is used as a connecting agent between browsers and security cameras.
• WebRTC is heavily used for real-time media.
• WebRTC provides the underlying connection between instructor and students for online education.
What are the pros and cons of WebRTC
The advantages of WebRTC include the following:
• Eliminates much of the in-house manual integration work required of IT
• Can adjust communication quality, bandwidth with traffic flow whenever network condition change
• Is supported by most major web browsers, including Google Chrome for desktop and Android, Mozilla Firefox for desktop and Android.
• Works on any operating system as long as the browser supports WebRTC.
• Does not require third-party components or plugins.
• Is free as open source software.
Disadvantages of WebRTC including the following:
• Each user must establish a P2P browser connection, making bandwidth an issue.
• Maintenance costs can be high because WebRTC requires powerful servers.
• Security and privacy standard are still unclear, leaving it up to IT departments to ensure that corporate security and privacy standards.
• There are no definitive quality of service standards, which means that quality of video or audio over the internet may be inconsistent.
Is WebRTC Secure
Every WebRTC software component is encrypted, and every WebRTC API requires secure origins via Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) or localhost. There are still open security questions that developers using WebRTC must consider. Signaling processing method, or the methods used to exchange metadata, are not specified for webRTC signaling. This means that developers must decide which security protocols to use and ensure that the protocols they select can be maintained with WebRTC.